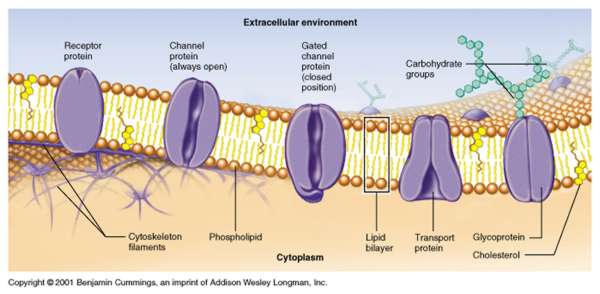
model mixed composition of phospholipids, glycolipds, sterols and proteins.
Adhesion Protein:
help the cell adhere to another or to a protein.
Communication Protein:
match up with identical proteins in the plasma membrane of an adjoining cell.
Receptor Protein:
Recognition Protein:
proteins identify a cell as nonself or self.
Passive transporter:
movement of particles across the cell membrane without an imput of energy.
Active transpoter:
movement of particles across the cell membrane with an imput of energy.
Difussion:
net movement of mocecules or ions down a concentration gradient.
Electric gradient:
a difference in electric charge between adjoining regions.
Pressure gradient:
a difference in pressure exerted per unit volume (area) between two adjoining regions.
Concentration gradient:
difference in the number per unit volume of molecules of a substance between adjoining regions.
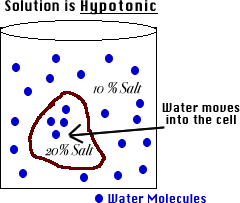
Hypotonic:
solution with lower solutes.
Hypertonic:
solution with more solutes.
Isotonic:
solutions that show no net osmotic movement.
Hydrastatic Pressure:
furgur pressure exerted by any volume of fluids.
Osmotic Presurre:
measure of tending of water to follows its water concentration gradient and move into that fluid.
Osmosis:
diflusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane, to a region where the water concentration is lower.
Endocytosis:
small patch of plasma membrane ballons inward and pinches off inside the cytoplasm.
Exocytosis:
a vesicle moves to the cell surface, and then the protein-studded lipid bilager of its membrane tuses with the plasma membrane.
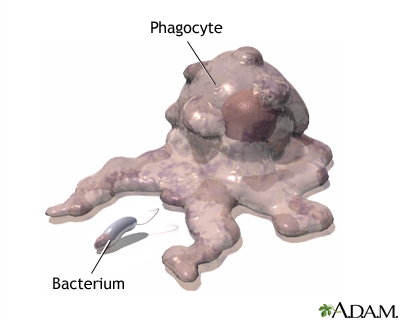
Phagocytosis:
common endocytic pathways.

















No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario